Alias (According to NCBI)
- RP11-69D4.1,
- 2-ALPHA-HSD,
- 20-ALPHA-HSD,
- C9,
- DD1,
- DDH,
- DDH1,
- H-37,
- HAKRC,
- MBAB,
- MGC8954
- 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase;
- aldo-keto reductase C;
- aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C1;
- chlordecone reductase homolog;
- dihydrodiol dehydrogenase 1;
- dihydrodiol dehydrogenase isoform DD1;
- hepatic dihydrodiol dehydrogenase;
- trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol dehydrogenase;
- type II 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- Converts progesterone to its inactive form, 20-alpha-dihydroxyprogesterone (20-alpha-OHP). In the liver and intestine, may have a role in the transport of bile. May have a role in monitoring the intrahepatic bile acid concentration. Has a low bile-binding ability. May play a role in myelin formation.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 10p15-p14
- Size: 14705 bp
- exons: 9
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000010.9
![]()
CGH (10p15): Losses (%) -12.8 Gain (%) 2.8
- HGMD :
- SNPs: 1645
mRNA sequence (Human): NM_001353.5
Size: 1384 bp
cDNA libraries: AKR1C1
- Size: 323 amino acids; 36788 Da
- Catalytic activity: 17-alpha,20-alpha-dihydroxypregn-4-en-3-one + NAD(P)+ = 17-alpha-hydroxyprogesterone + NAD(P)H.
Trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol + NADP+ = catechol + NADPH.
Subcellular location: Cytoplasm.
Protein domains

Pathway: AKR1C1
Protein interactions: AKR1C1
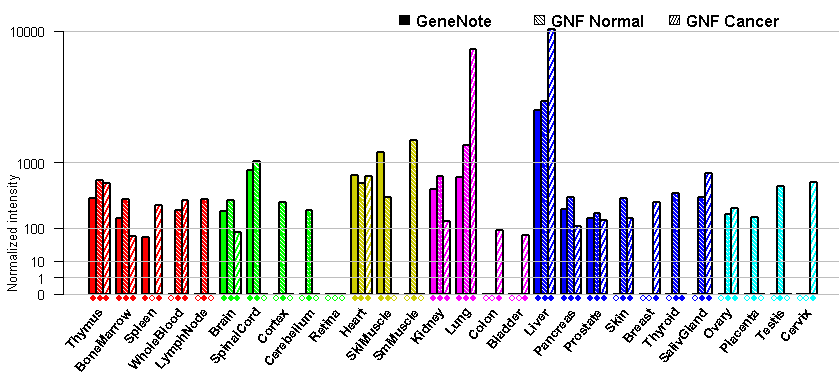
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA):
- OMIM : 600449
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy