Alias (According to NCBI)
- K60;
- NAF;
- GCP1;
- LECT;
- LUCT;
- NAP1; neutrophil-activating peptide 1
- 3-10C;
- CXCL8;
- GCP-1;
- LYNAP; lymphocyte-derived neutrophil-activating factor
- MDNCF; monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor
- MONAP;
- SCYB8; small inducible cytokine subfamily B, member 8
- TSG-1;
- AMCF-I;
- b-ENAP
- emoctakin
- T cell chemotactic factor
- chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 8
- beta-thromboglobulin-like protein
- granulocyte chemotactic protein 1
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- IL-8 is a chemotactic factor that attracts neutrophils, basophils, and T-cells, but not monocytes. It is also involved in neutrophil activation. It is released from several cell types in response to an inflammatory stimulus. IL-8(6-77) has a 5-10-fold higher activity on neutrophil activation, IL-8(5-77) has increased activity on neutrophil activation and IL-8(7-77) has a higher affinity to receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2 as compared to IL-8(1-77), respectively.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 4q13-q21
- Size: 3159 bp
- exons: 4
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000004

CGH (4q13): Losses (%) -17.9 Gain (%) 2.2
- Size:99 amino acids; 11098 Da
Subcellular location: secreted
SUBUNIT: Homodimer.
Protein domains
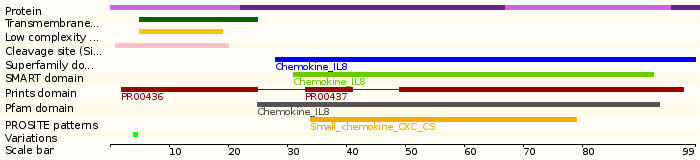
Protein sequence (Human): P10145
Homologous genes: 47937
2D PAGE:il8
3D Structure: 3IL8 1ICW 1QE6 1ILQ 1ILP 1ROD 1IKL 1IKM
1IL8 2IL8PTM: Several N-terminal processed forms are produced by proteolytic cleavage after secretion from at least peripheral blood monocytes, leukcocytes and endothelial cells. In general, IL-8(1-77) is referred to as interleukin-8. IL-8(6-77) is the most promiment form IL8
Protein interactions: IL8_HUMAN
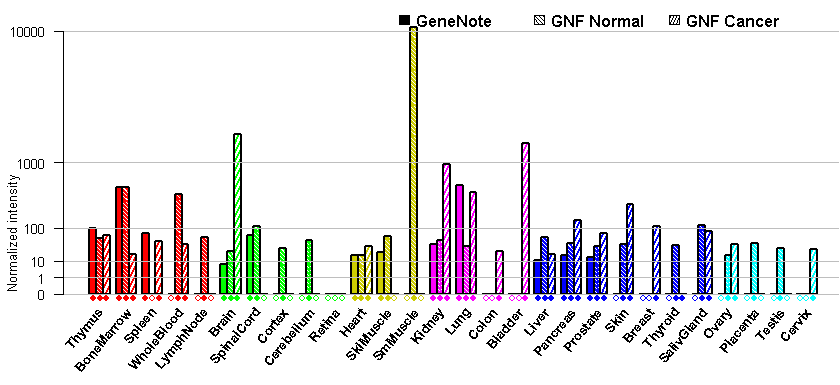
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): IL8
- OMIM : 146930
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy