Alias (According to NCBI)
- FSH-releasing protein;
- Inhibin, beta-1;
- erythroid differentiation factor;
- follicle-stimulating hormone-releasing protein;
- inhibin beta A;
- inhibin, beta A (activin A, activin AB alpha polypeptide)
- EDF,
- FRP
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- Inhibins and activins inhibit and activate, respectively, the secretion of follitropin by the pituitary gland. Inhibins/activins are involved in regulating a number of diverse functions such as hypothalamic and pituitary hormone secretion, gonadal hormone secretion, germ cell development and maturation, erythroid differentiation, insulin secretion, nerve cell survival, embryonic axial development or bone growth, depending on their subunit composition. Inhibins appear to oppose the functions of activins.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 7p15-p13
- Size: 14106 bp
- exons: 2
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000007.12
![]()
CGH (7q15-p13): Losses (%) -1.1 Gain (%) 13.4
mRNA sequence (Human): NM_002192.2
Size: 2175 bp
cDNA libraries: INHBA
- Size: 426 amino acids; 47442 Da
- Catalytic activity:
Subcellular location: Secreted
Protein domains

Protein interactions: INHBA
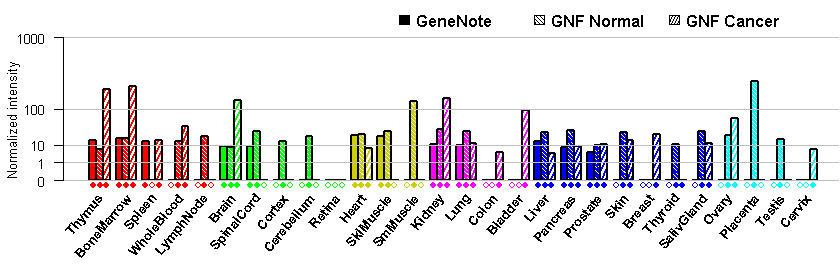
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): HPA020031
- OMIM : 147290
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy