Alias (According to NCBI)
- COCA1,
- FCC1,
- HNPCC,
- HNPCC1
- mutS homolog 2
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- Component of the post-replicative DNA mismatch repair system (MMR). Forms two different heterodimers: MutS alpha (MSH2-MSH6 heterodimer) and MutS beta (MSH2-MSH3 heterodimer) which binds to DNA mismatches thereby initiating DNA repair. When bound, heterodimers bend the DNA helix and shields approximately 20 base pairs. MutS alpha recognizes single base mismatches and dinucleotide insertion-deletion loops (IDL) in the DNA. MutS beta recognizes larger insertion-deletion loops up to 13 nucleotides long. After mismatch binding, MutS alpha or beta forms a ternary complex with the MutL alpha heterodimer, which is thought to be responsible for directing the downstream MMR events, including strand discrimination, excision, and resynthesis. ATP binding and hydrolysis play a pivotal role in mismatch repair functions. The ATPase activity associated with MutS alpha regulates binding similar to a molecular switch: mismatched DNA provokes ADP-->ATP exchange, resulting in a discernible conformational transition that converts MutS alpha into a sliding clamp capable of hydrolysis-independent diffusion along the DNA backbone. This transition is crucial for mismatch repair. MutS alpha may also play a role in DNA homologous recombination repair. In melanocytes may modulate both UV-B-induced cell cycle regulation and apoptosis.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
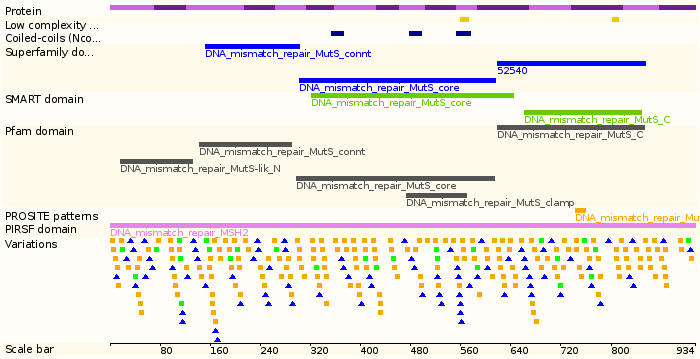
- Location: 2p22-p21
- Size: 80098 bp
- exons: 16
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000002.10
![]()
CGH (2p22): Losses (%) -2.2 Gain (%) 5.6
mRNA sequence (Human): NM_000251.1
Size: 3145 bp
cDNA libraries: MSH2
- Size: 934 amino acids; 104743 Da
- Subunit: Heterodimer consisting of MSH2-MSH6 (MutS alpha) or MSH2-MSH3 (MutS beta). Both heterodimer form a ternary complex with MutL alpha (MLH1-PMS1). Interacts with EXO1. Part of the BRCA1-associated genome surveillance complex (BASC), which contains BRCA1, MSH2, MSH6, MLH1, ATM, BLM, PMS2 and the RAD50-MRE11-NBS1 protein complex. This association could be a dynamic process changing throughout the cell cycle and within subnuclear domains. Interacts with ATR.:
Subcellular location: Nucleus
Protein domains
Pathway:
Colorectal cancer
Protein interactions: MSH2
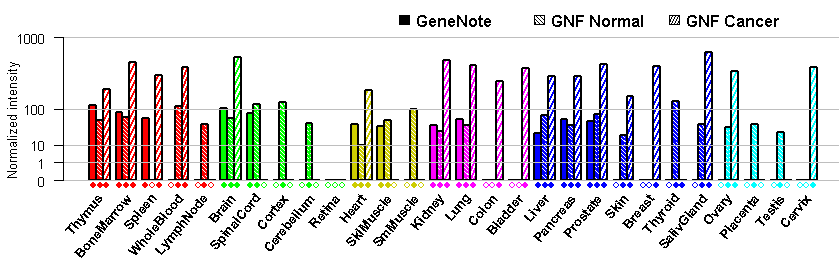
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB009572
- OMIM : 609309
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy