Alias (According to NCBI)
- HHM,
- MGC14611,
- PLP,
- PTHR,
- PTHRP
- PTH-related protein;
- humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy;
- osteostatin;
- parathyroid hormone-like protein;
- parathyroid hormone-like related protein;
- parathyroid hormone-related protein;
- parathyroid-like protein
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- Neuroendocrine peptide which is a critical regulator of cellular and organ growth, development, migration, differentiation and survival and of epithelial calcium ion transport. Regulates endochondral bone development and epithelial-mesenchymal interactions during the formation of the mammary glands and teeth.
- Osteostatin is a potent inhibitor of osteoclastic bone resorption.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 12p12.1-p11.2
- Size: 16900 bp
- exons:
Transcript variant 1: 3
Transcript variant 2 2
Transcript variant 3: 2
Transcript variant 4: 3
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000012.10
![]()
CGH (12p12.1): Losses (%) -5.0 Gain (%) 7.8
- HGMD :
- SNPs: 5744
mRNA sequence (Human):
Transcript variant 1: NM_198965.1
Transcript variant 2: NM_002820.2
Transcript variant 3 NM_198964.1
Transcript variant 4: NM_198966.1
Size:
Transcript varient 1: 1331
Transcript varient 2 1881
Transcript varient 3 1862
Transcript varient 4: 1312
cDNA libraries: PTHLH
- Size: 177 amino acids; 20194 Da
- Catalytic activity:
Subcellular location: Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Secreted
Protein domains
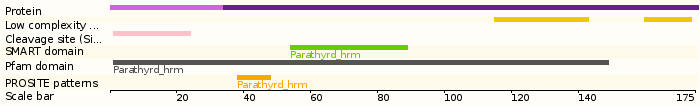
Protein sequence (Human): P12272
Homologous genes: 2113
2D PAGE: PTHLH
3D Structure: 1BZG
PTM: PTHLH (There are 3 principal secretory forms, called PTHrP[1-36], PTHrP[38-94], and osteostatin (PTHrP[107-139]) arising from endoproteolytic cleavage of the initial translation product. Each of these secretory forms is believed to have one or more of its own receptors that mediates the normal paracrine, autocrine and endocrine actions.)
- Pathways and interactions (According to PIR)
Pathway:
Protein interactions: PTHLH

- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB000072
- OMIM : 168470
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy