Alias (According to NCBI)
- C-Rel
- C-Rel proto-oncogene protein;
- oncogene REL, avian reticuloendotheliosis;
- v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog;
- v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- Proto-oncogene that may play a role in differentiation and lymphopoiesis. NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. The NF-kappa-B heterodimer RELA/p65-c-Rel is a transcriptional activator.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 2p13-p12
- Size: 41427 bp
- exons:
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000002.10
![]()
CGH (2p13): Losses (%) -2.2 Gain (%) 5.0
- HGMD :
- SNPs: 5966
mRNA sequence (Human): NM_002908.2
Size: 2592 bp
cDNA libraries:
- Size: 619 amino acids: 68520 Da
- Catalytic activity:
Subcellular location: Nucleus
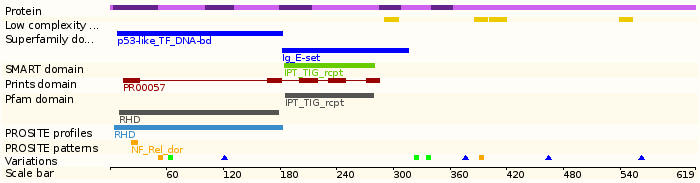
Protein domains
Pathway:
Protein interactions: REL
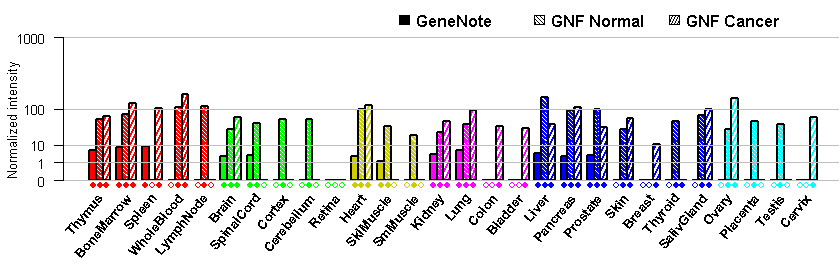
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB004404
- OMIM : 164910
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy