Alias (According to NCBI)
- RP1-261G23.1,
- MGC70609,
- VEGF,
- VEGF-A,
- VPF
- vascular permeability factor
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- Growth factor active in angiogenesis, vasculogenesis and endothelial cell growth. Induces endothelial cell proliferation, promotes cell migration, inhibits apoptosis, and induces permeabilization of blood vessels. Binds to the VEGFR1/Flt-1 and VEGFR2/Kdr receptors, heparan sulfate and heparin. Neuropilin-1 binds isoforms VEGF-165 and VEGF-145.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 6p12
- Size: 16272 bp
- exons:
- Transcript variant1: 8
- Transcript variant2: 8
- Transcript variant3: 8
- Transcript variant4: 7
- Transcript variant5: 7
- Transcript variant6: 6
- Transcript variant7: 7
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000006.10

CGH (16p12): Losses (%) -1.7 Gain (%) 7.0
- HGMD :
- SNPs: 7422
mRNA sequence (Human):
Transcript variant1: NM_001025366.1
Transcript variant2: NM_003376.4
Transcript variant3: NM_001025367.1
Transcript variant4: NM_001025368.1
Transcript variant5: NM_001025369.1
Transcript variant6: NM_001025370.1
Transcript variant7: NM_001033756.1
Size:
Transcript variant1: 3665 bp
Transcript variant2: 3614 bp
Transcript variant3: 3596 bp
Transcript variant4: 3542 bp
Transcript variant5: 3507 bp
Transcript variant6: 3410 bp
Transcript variant7: 3476 bp
cDNA libraries:
- Size: 232 amino acids: 27042 Da
- Catalytic activity:
Subcellular location: Secreted. Note=VEGF121 is acidic and freely secreted. VEGF165 is more basic, has heparin-binding properties and, although a signicant proportion remains cell-associated, most is freely secreted. VEGF189 is very basic, it is cell-associated after secretion and is bound avidly by heparin and the extracellular matrix, although it may be released as a soluble form by heparin, heparinase or plasmin.
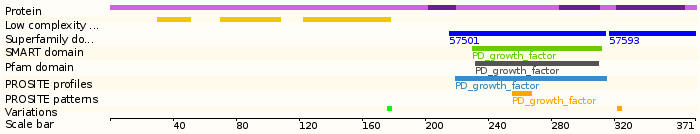
Protein domains
Pathway:
Kegg hsa04060 Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction
Kegg hsa04150 mTOR signaling pathway
Kegg hsa04370 VEGF signaling pathway
Kegg hsa04510 Focal adhesion
Kegg hsa05211 Renal cell carcinoma
Kegg hsa05212 Pancreatic cancer
Kegg hsa05219 Bladder cancerBioCarta Actions of Nitric Oxide in the Heart
BioCarta Hypoxia-Inducible Factor in the Cardiovascular System
BioCarta VEGF, Hypoxia, and Angiogenesis
Protein interactions: VEGF

- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB005429
- OMIM : 192240
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy