Alias (According to NCBI)
- DP2
- DP2.5
- DP3
- FAP
- FPC
- GS
- adenomatosis polyposis coli
- Adenomatous polyposis coli protein (APC protein).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
The metabolic function of the APC gene is not known. Defects in this gene cause familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), an autosomal dominant pre-malignant disease that usually progresses to malignancy. Disease-associated mutations tend to be clustered in a small region designated the mutation cluster region (MCR) and result in a truncated protein product.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 5q21-q22
- Orientation: Plus strand
- Size:108,049 bases
- 16 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_034772
![]()
CGH (5q21-q22): Losses (%) -23.5 Gain (%) 3.4
- Size: 2843 amino acids; 311658 Da
- Protein domains:
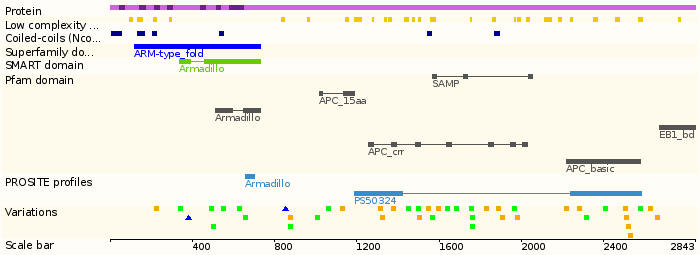
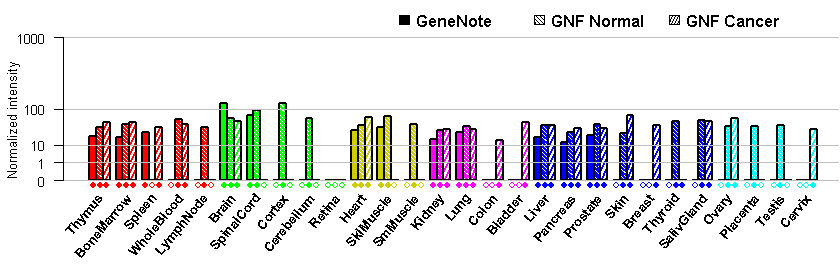
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA) : CAB002211
- OMIM: 175100
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy