Alias (According to NCBI)
- ATP2B
- DAR
- DD
- MGC45367
- SERCA2
- ATPase, Ca++ dependent, slow-twitch, cardiac muscle-2
- ATPase, Ca++ transporting, cardiac muscle, slow twitch 2
- Darier disease (keratosis follicularis)
- SR Ca(2+)-ATPase 2
- calcium pump 2
- calcium-transporting ATPase sarcoplasmic reticulum type, slow twitch skeletal muscle isoform
- endoplasmic reticulum class 1/2 Ca(2+) ATPase
- sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2
- Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 (EC 3.6.3.8) (Calcium pump 2) (SERCA2) (SR Ca(2+)-ATPase 2) (Calcium-transporting ATPase sarcoplasmic reticulum type, slow twitch skeletal muscle isoform) (Endoplasmic reticulum class 1/2 Ca(2+) ATPase).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
This gene encodes one of the SERCA Ca(2+)-ATPases, which are intracellular pumps located in the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticula of muscle cells. This enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen, and is involved in regulation of the contraction/relaxation cycle. Mutations in this gene cause Darier-White disease, also known as keratosis follicularis, an autosomal dominant skin disorder characterized by loss of adhesion between epidermal cells and abnormal keratinization.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 12q23-q24.1
- Orientation: Plus strand
- Size: 69,463 bases
- 22 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_009775
![]()
- CGH (12q23 - 24.1): Losses (%) -0.6 Gain (%) 3.4
- Size:1042 amino acids; 114756 Da
- Sub cellular location: Integral membrane protein. Sarcoplasmic and endoplasmic reticulum.
- Catalytic activity: ATP + H(2)O + Ca(2+)(Cis) = ADP + phosphate + Ca(2+)(Trans)
- Protein domains:

- Pathways:
- Interactions:
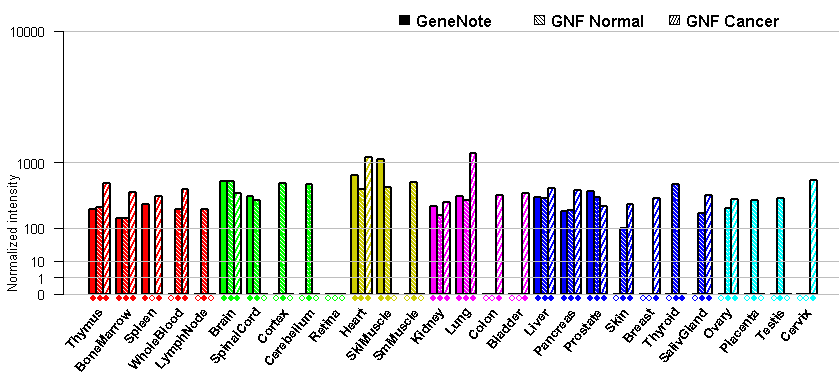
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA):
- OMIM:108740
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy