Alias (According to NCBI)
- ATPMB
- ATPSB
- MGC5231
- ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, beta polypeptide
- mitochondrial ATP synthetase, beta subunit
- ATP synthase beta chain, mitochondrial precursor (EC 3.6.3.14).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- This gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. ATP synthase is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, comprising the proton channel. The catalytic portion of mitochondrial ATP synthase consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled with a stoichiometry of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and a single representative of the other 3. The proton channel consists of three main subunits (a, b, c). This gene encodes the beta subunit of the catalytic core.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 12q13.13
- Orientation: minus strand
- Size: 7,891 bp
- 9 exons
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000012
CGH (12q13.13): Losses (%) -1.7 Gain (%) 8.4
HGMD:
- SNP: ATP5B
- Size: 529 amino acids; 56560 Da
- Catalytic activity: ATP + H(2)O + H(+)(In) = ADP + phosphate + H(+)(Out).
- Subcellular location: Mitochondrial.
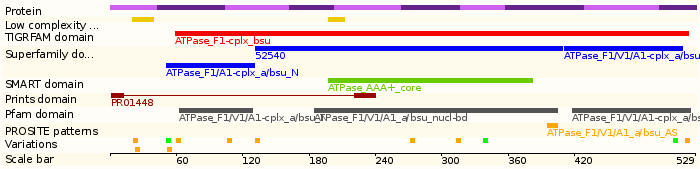
- Protein domains
- Pathway: Electron transport
- Protein interactions:
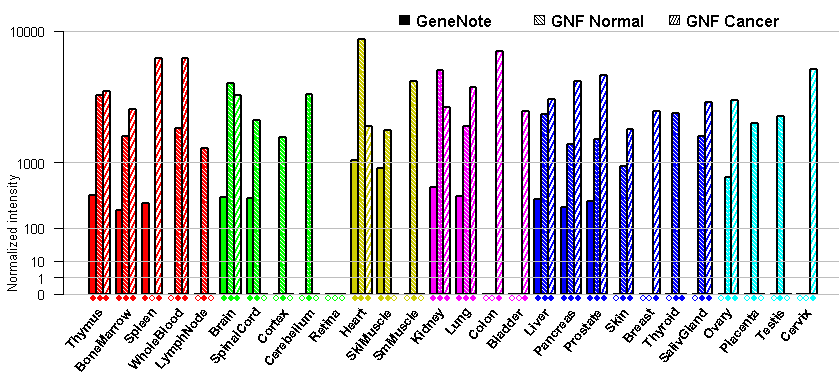
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): HPA001528
OMIM: 102910
PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy