Alias (According to NCBI)
- BCL2-associated X protein
- apoptosis regulator BAX
- Apoptosis regulator BAX, membrane isoform alpha.
- Apoptosis regulator BAX, Cytoplasmic isoform beta.
- BAX protein, Cytoplasmic isoform gamma.
- BAX protein, Cytoplasmic isoform delta.
Description
(According to SwissProt)
This protein forms a heterodimer with BCL2, and functions as an apoptotic activator. This protein is reported to interact with, and increase the opening of, the mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), which leads to the loss in membrane potential and the release of cytochrome c. The expression of this gene is regulated by the tumor suppressor P53 and has been shown to be involved in P53-mediated apoptosis. Accelerates programmed cell death by binding to, and antagonizing the apoptosis repressor BCL2 or its adenovirus homolog E1B 19k protein.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location:19q13.3-13.4
- Orientation: Plus strand
- Size:6,920 bases
- 7 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_011109
![]()
- CGH (19q13.3 - 13.4): Losses (%) -6.1 Gain (%) 5.0
| Name | Size | Location | sequence |
| Apoptosis regulator BAX, membrane isoform alpha | 192 amino acids; 21184 Da | Membrane bound | Q07812 |
| Apoptosis regulator BAX, Cytoplasmic isoform beta | 218 amino acids; 24220 Da | Cytoplasmic | Q07814 |
| BAX protein, Cytoplasmic isoform gamma | 41 amino acids; 4678 Da | Cytoplasmic | Q07815 |
| BAX protein, Cytoplasmic isoform delta | 143 amino acids; 15772 Da | Cytoplasmic | P55269 |
- Protein domains:

- Pathways: Apoptotic Signaling in Response to DNA Damage
- Ceramide Signaling Pathway
- Hypoxia and p53 in the Cardiovascular system
- p53 Signaling Pathway
- Regulation of BAD phosphorylation
- Role of Mitochondria in Apoptotic Signaling
- Interactions:
Apoptosis regulator BAX, membrane isoform alpha Q07812
Apoptosis regulator BAX, Cytoplasmic isoform beta Q07814
BAX protein, Cytoplasmic isoform gamma Q07815
BAX protein, Cytoplasmic isoform delta P55269
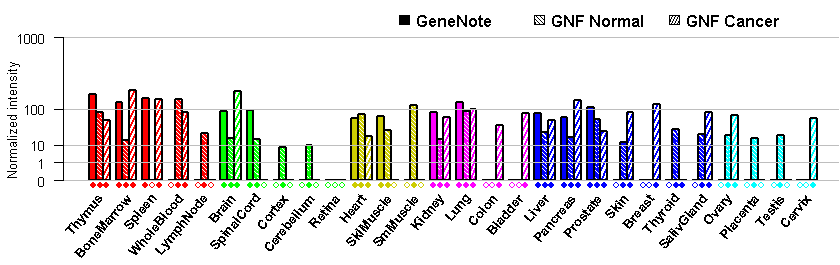
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB004206
- OMIM: 600040
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy