Alias (According to NCBI)
- CFB
- GBG
- PBF2
- B-factor, properdin
- C3 proaccelerator
- C3 proactivator
- C3/C5 convertase
- glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein
- Complement factor B precursor (EC 3.4.21.47) (C3/C5 convertase)
(Properdin factor B) (Glycine-rich
beta glycoprotein) (GBG) (PBF2).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- This gene encodes complement factor B, a component of the alternative pathway of complement activation. Factor B circulates in the blood as a single chain polypeptide. Upon activation of the alternative pathway, it is cleaved by complement factor D yielding the noncatalytic chain Ba and the catalytic subunit Bb. The active subunit Bb is a serine protease which associates with C3b to form the alternative pathway C3 convertase. Bb is involved in the proliferation of preactivated B lymphocytes, while Ba inhibits their proliferation. This gene localizes to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6. This cluster includes several genes involved in regulation of the immune reaction. The polyadenylation site of this gene is 421 bp from the 5' end of the gene for complement component 2.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 6p21.3
- Orientation: plus strand
- Size:6079 bp
- 18 exons
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000006.
CGH (6p21.3): Losses (%) -1.1 Gain (%) 9.5 Amplifications 0.0
- HGMD :
- SNPs: BF
mRNA sequence (Human): NM_001710.
Size: 2565 bp
cDNA libraries: BF
- Size: 764 amino acids; 85532 Da
- Catalytic activity: Cleavage of Arg-|-Ser bond in complement component C3 alpha-chain to yield C3a and C3b, and Arg-|-Xaa bond in complement component C5 alpha-chain to yield C5a and C5b.
Subcellular location: Secreted.
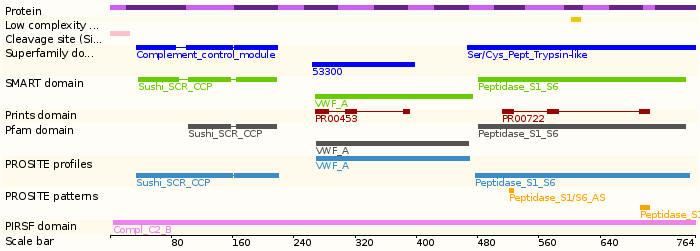
Protein domains
Pathway: Alternative Complement Pathway
Protein Interactions:
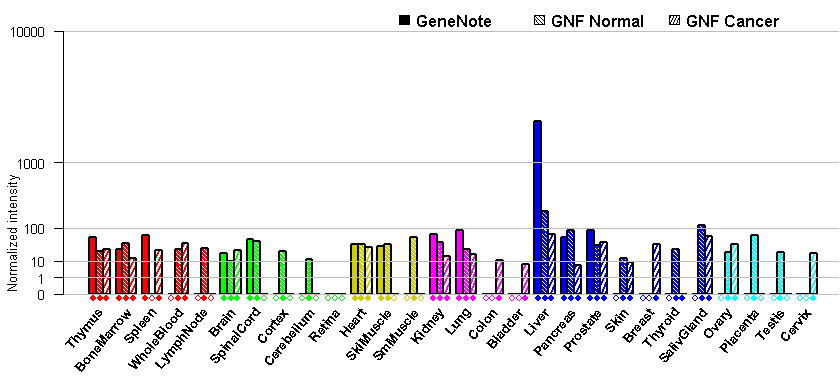
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): HPA001817
