Alias (According to NCBI)
- CD1
- CD1A antigen, a polypeptide
- T-cell surface antigen T6/Leu-6
- T-cell surface glycoprotein CD1a precursor
- hTa1 thymocyte antigen
- thymocyte antigen CD1A
- T-cell surface glycoprotein CD1a precursor (CD1a
antigen) (T-cell surface antigen T6/Leu-6) (hTa1
thymocyte antigen).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- This gene encodes a member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins, which are structurally related to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins and form heterodimers with beta-2-microglobulin. The CD1 proteins mediate the presentation of primarily lipid and glycolipid antigens of self or microbial origin to T cells. The human genome contains five CD1 family genes organized in a cluster on chromosome 1. The CD1 family members are thought to differ in their cellular localization and specificity for particular lipid ligands. The protein encoded by this gene localizes to the plasma membrane and to recycling vesicles of the early endocytic system. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed, but their biological validity has not been determined.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 1q22-q23
- Orientation: plus strand
- Size: 4109 bp
- 6 exons
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000001
![]()
CGH (1q22-q23): Losses (%) -1.1 Gain (%) 8.9
- HGMD (Human Gene Mutation Database):
- All SNPs: CD1A
- Size: 327 amino acids; 37172 Da
- Catalytic activity:
Subcellular location: Type I membrane protein.
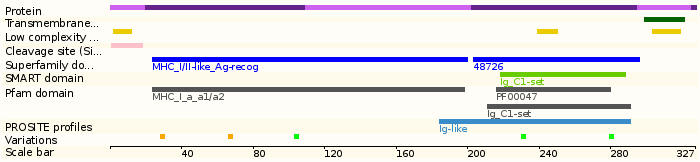
Protein domains
Pathway:
Protein interactions:
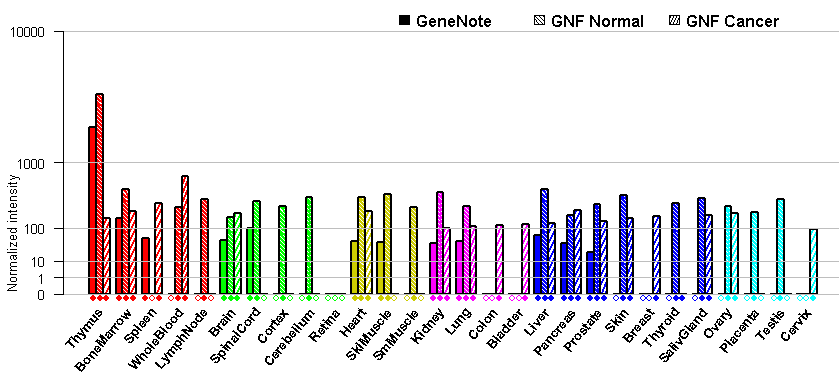
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA) : CAB000009
OMIM: 188370
PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy