Alias (According to NCBI)
- CE-2
- hCE-2
- iCE
- carboxylesterase 2 (intestine, liver)
- intestinal carboxylesterase; liver carboxylesterase-2
- Carboxylesterase 2 precursor (EC 3.1.1.1) (CE-2) (hCE-2).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
Carboxylesterase 2 is a member of a large multigene family. The enzymes encoded by these genes are responsible for the hydrolysis of ester- and amide-bond-containing drugs such as cocaine and heroin. They also hydrolize long-chain fatty acid esters and thioesters. The specific function of this enzyme has not yet been determined; however, it is speculated that carboxylesterases may play a role in lipid metabolism and/or the blood-brain barrier system. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
CGH (16q22.1): Losses (%) -3.4 Gain (%) 7.8
- HGMD (Human Gene Mutation Database):
- SNPs: CES2
- Size: 559 amino acids; 61806 Da
- Catalytic activity: A carboxylic ester + H(2)O = an alcohol + a carboxylic anion.
Subcellular location: Endoplasmic reticulum lumen
Protein domains

Pathway:
Protein interactions:
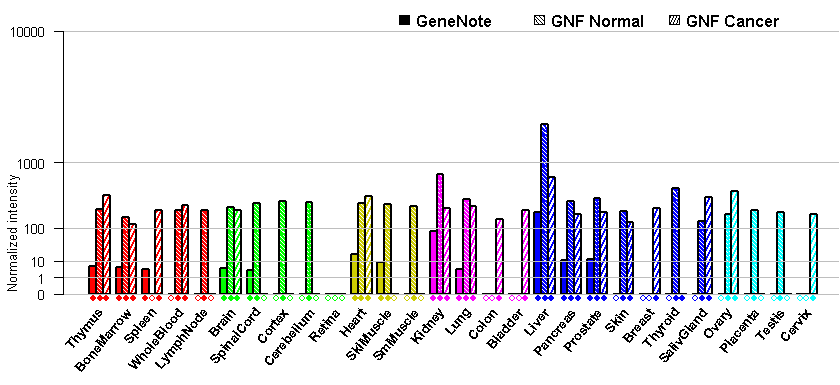
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA) : HPA018897
OMIM: 605278
PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy