Alias (According to NCBI)
- COX1
- PGHS-1
- PTGHS
- prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase)
- Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 precursor (EC 1.14.99.1) (Cyclooxygenase -1) (COX-1) (Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1) (Prostaglandin H2 synthase 1) (PGH synthase 1) (PGHS-1) (PHS 1).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase (PTGS), also known as cyclooxygenase, is the key enzyme in prostaglandin biosynthesis, and acts both as a dioxygenase and as a peroxidase. This gene encodes PTGS1, which regulates angiogenesis in endothelial cells, and is inhibited by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin. PTGS1 is thought to be involved in cell-cell signaling and maintaining tissue homeostasis. May play an important role in regulating or promoting cell proliferation in some normal and neoplastically transformed cells.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location:9q32-q33.3
- Orientation: Plus strand
- Size: 24,752 bases
- 11 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_008470
![]()
- CGH ( 9q32-33.3) : Losses (%) -3.4 Gain (%) 8.9
- HGMD:
- SNPs: Cox1
- Size:599 amino acids; 68656 Da
- Catalytic activity: Arachidonate + AH(2) + 2 O(2) = prostaglandin H2 + A + H(2)O
- Sub cellular location: Membrane-associated. Microsomal membrane
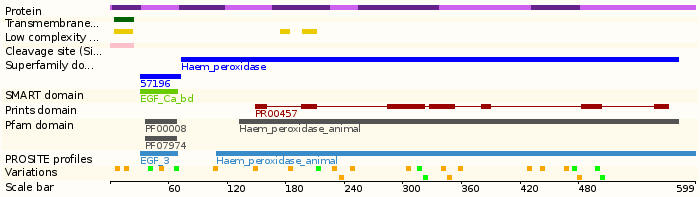
- Protein domains:
- Pathways: Aspirin Blocks Signaling Pathway Involved in Platelet Activation
- Mechanism of Acetaminophen Activity and Toxicity
- Mechanism of Gene Regulation by Peroxisome Proliferators via PPARa(alpha)
- Interactions: P23219
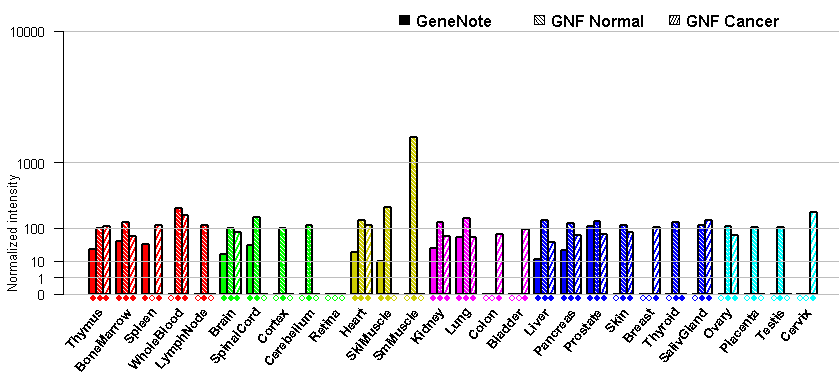
- OMIM:176805
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy