Alias (According to NCBI)
- EphB4
- HTK
- MYK1
- TYRO11
- Tyro11
- ephrin receptor EphB4
- hepatoma transmembrane kinase
- Ephrin type-B receptor 4 precursor (EC 2.7.1.112) (Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor HTK)
Description
(According to SwissProt)
Ephrin receptors and their ligands, the ephrins, mediate numerous developmental processes, particularly in the nervous system. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. Ephrin receptors make up the largest subgroup of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. The protein encoded by this gene binds to ephrin-B2 and plays an essential role in vascular development.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 7q22
- Orientation: Minus strand
- Size:24,840 bases
- 17 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_007933
![]()
CGH (7q22): Losses (%) -2.8 Gain (%) 12.3
- HGMD:
- SNPs: EPHB4
- Size: 987 amino acids; 108269 Da
- Sub cellular location: Type I membrane protein
- Catalytic activity: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate
- Protein domains:

- Pathways:
- Interactions:
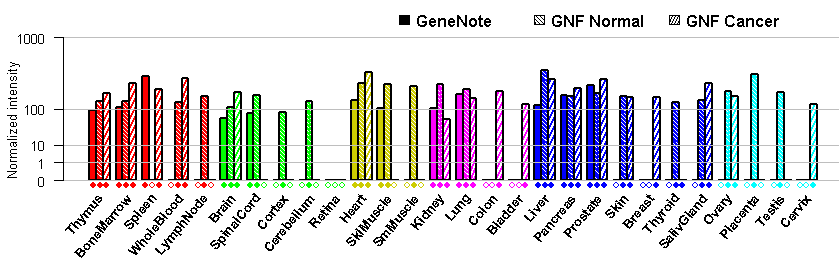
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB013537
- OMIM:600011
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy