Alias (According to NCBI)
- MAT-8
- MAT8
- PLML
- FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 3
- FXYD domain-containing ion transport regulator 3
- phospholemman-like protein
- phospholemman-like, expressed in breast tumors, 8kD
- FXYD domain-containing ion transport regulator 3 precursor (Chloride
conductance inducer protein
Mat-8) (Mammary tumor 8 kDa protein) (Phospholemman-like).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
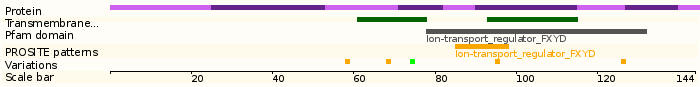
- This gene encodes a member of a family of small membrane proteins that share a 35-amino acid signature sequence domain, beginning with the sequence PFXYD and containing 7 invariant and 6 highly conserved amino acids. The approved human gene nomenclature for the family is FXYD-domain containing ion transport regulator. Mouse FXYD5 has been termed RIC (Related to Ion Channel). FXYD2, also known as the gamma subunit of the Na,K-ATPase, regulates the properties of that enzyme. FXYD1 (phospholemman), FXYD2 (gamma), FXYD3 (MAT-8), FXYD4 (CHIF), and FXYD5 (RIC) have been shown to induce channel activity in experimental expression systems. Transmembrane topology has been established for two family members (FXYD1 and FXYD2), with the N-terminus extracellular and the C-terminus on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. The protein encoded by this gene may function as a chloride channel or as a chloride channel regulator. Two transcript variants encode two different isoforms of the protein; in addition, transcripts utilizing alternative polyA signals have been described in the literature.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 19q13.11-q13.12
- Orientation: plus strand
- Size: 8429 bp
- 9 exons
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000019
![]()
CGH (19q 13.11-13.12) : Losses (%) -6.1 Gain (%) 5.0
- HGMD :
- SNPs: FXYD3
- Size: 87 amino acids; 9263 Da
- Catalytic activity:
Subcellular location: Type I membrane protein (Potential).
Protein domains
Pathway:
Protein interactions:
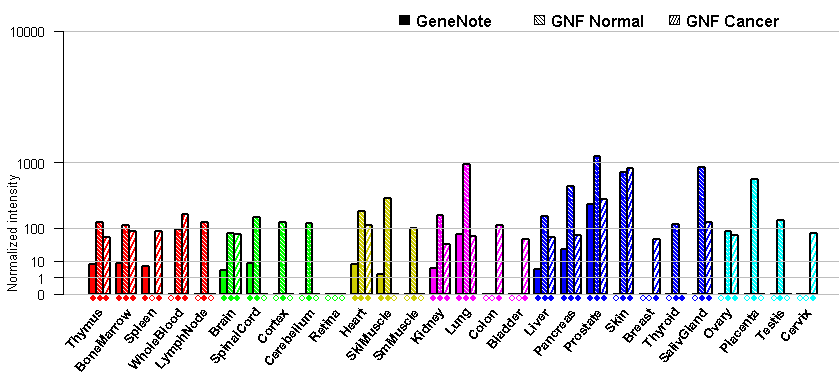
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): HPA010856
OMIM: 604996
PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy