Alias (According to NCBI)
- GST1
- GSTM1-1
- GSTM1a-1a
- GSTM1b-1b
- GTH4
- GTM1
- H-B
- MGC26563
- MU
- MU-1
- GST class-mu 1
- HB subunit 4
- S-(hydroxyalkyl)glutathione lyase
- glutathione S-alkyltransferase
- glutathione S-aralkyltransferase
- glutathione S-aryltransferase
- glutathione S-transferase M1
- glutathione S-transferase, Mu-1
- Glutathione S-transferase Mu 1 (EC 2.5.1.18) (GSTM1-1) (HB subunit 4) (GTH4) (GSTM1a-1a) (GSTM1b-1b) (GST class-mu 1).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
Cytosolic and membrane-bound forms of glutathione S-transferase are encoded by two distinct supergene families. This gene encodes a glutathione S-transferase that belongs to the mu class. The mu class of enzymes functions in the detoxification of electrophilic compounds, including carcinogens, therapeutic drugs, environmental toxins and products of oxidative stress, by conjugation with glutathione. These genetic variations can change an individual's susceptibility to carcinogens and toxins as well as affect the toxicity and efficacy of certain drugs. Null mutations of this class mu gene have been linked with an increase in a number of cancers, likely due to an increased susceptibility to environmental toxins and carcinogens.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location:1p13.3
- Orientation: Plus strand
- Size: 5,925 bases
- 8 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_019273
![]()
CGH (1p13.3): Losses (%) -8.4 Gain (%) 2.2
- Size:217 amino acids; 25580 Da
- Sub cellular location: Cytoplasmic
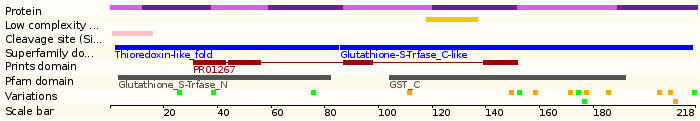
- Protein domains:
- Pathways: Multi-Drug Resistance Factors
- Interactions:
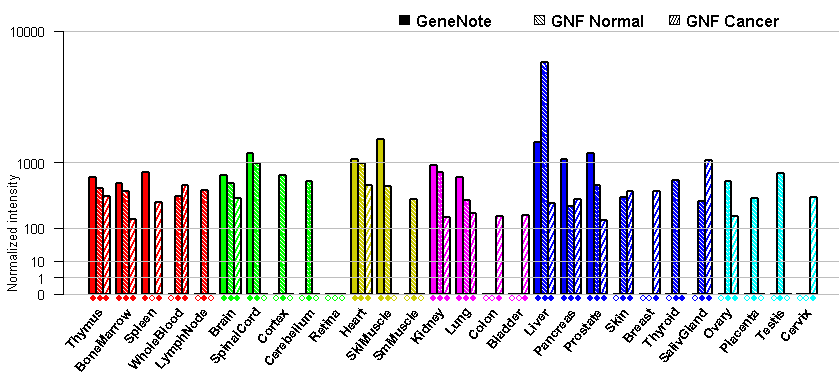
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB022669
- OMIM: 138350
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy