Alias (According to NCBI)
- beta-globin
- hemoglobin
- beta globin chain
- beta globin mutant
- hemoglobin beta chain
- hemoglobin, beta
- Hemoglobin beta chain.
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- The alpha (HBA) and beta (HBB) loci
determine the structure of the 2 types of polypeptide chains in adult hemoglobin, Hb A.
The normal adult hemoglobin tetramer consists of two alpha chains and two beta chains.
Mutant beta globin causes sickle cell anemia. Absence of beta chain causes
beta-zero-thalassemia. Reduced amounts of detectable beta globin causes
beta-plus-thalassemia. The order of the genes in the beta-globin cluster is 5'-epsilon --
gamma-G -- gamma-A -- delta -- beta--3'.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 11p15.5
- Orientation: minus strand
- Size:1606 bp
- 3 exons
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000011.
CGH (11p15.5): Losses (%) -11.7 Gain (%) 2.2
- Size: 146amino acids; 15867 Da
- Catalytic activity:
· Subcellular location: intracellular, cytoplasm
· Protein domains:

Pathway:
Protein interactions:
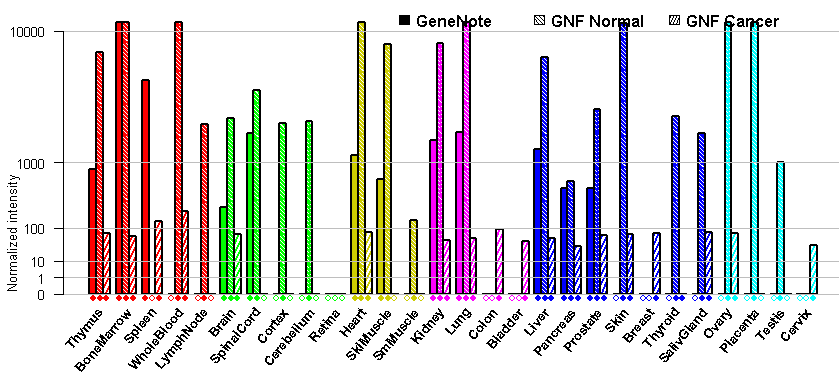
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB009526
OMIM: 141900
PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy