Alias (According to NCBI)
- N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase
- TSD
- beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase
- hexosaminidase A (alpha polypeptide)
- Beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain precursor (EC 3.2.1.52) (N-acetyl-
beta-glucosaminidase)
(Beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase) (Hexosaminidase A).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- Hexosaminidase A is the alpha subunit of the lysosomal enzyme beta-hexosaminidase that, together with the cofactor GM2 activator protein, catalyzes the degradation of the ganglioside GM2, and other molecules containing terminal N-acetyl hexosamines. Beta-hexosaminidase is composed of two subunits, alpha and beta, which are encoded by separate genes. Both beta-hexosaminidase alpha and beta subunits are members of family 20 of glycosyl hydrolases. Mutations in the alpha or beta subunit genes lead to an accumulation of GM2 ganglioside in neurons and neurodegenerative disorders termed the GM2 gangliosidoses. Alpha subunit gene mutations lead to Tay-Sachs disease (GM2-gangliosidosis type I).
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 15q23-q24
- Orientation: minus strand
- Size: 32561 bp
- 14 exons
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000015
![]()
CGH (15q23-24): Losses (%) -1.7 Gain (%) 8.4
- Size: 529 amino acids; 60688 Da
- Catalytic activity:
Subcellular location: Lysosomal.
Protein domains

Pathway:
Protein interactions:
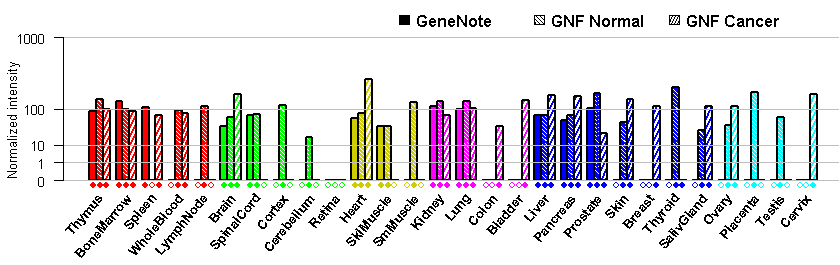
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): HEXA
OMIM: 606869
PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy