Alias (According to NCBI)
- HIF-1ALPHA
- HIF-1alpha
- HIF1-ALPHA
- MOP1
- ARNT interacting protein
- hypoxia-inducible factor 1, alpha subunit (basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor)
- member of PAS superfamily 1
- Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1 alpha) (HIF1 alpha) (ARNT interacting protein) (Member of PAS protein 1) (MOP1).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF1) is a transcription factor found in mammalian cells cultured under reduced oxygen tension that plays an essential role in cellular and systemic homeostatic responses to hypoxia. HIF1 is a heterodimer composed of an alpha subunit and a beta subunit. The beta subunit has been identified as the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT). This gene encodes the alpha subunit of HIF-1. Overexpression of a natural antisense transcript (aHIF) of this gene has been shown to be associated with nonpapillary renal carcinomas.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location:14q21-q24
- Orientation: Plus strand
- Size: 52,737 bases
- 15 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_026437
![]()
CGH (14q21-24): Losses (%) -3.4 Gain (%) 6.7
- HGMD:
- SNP: HIF1A
- Size: 826 amino acids; 92670 Da
- Sub cellular location: Cytoplasmic in normoxia, nuclear translocation in response to hypoxia
- Protein domains:
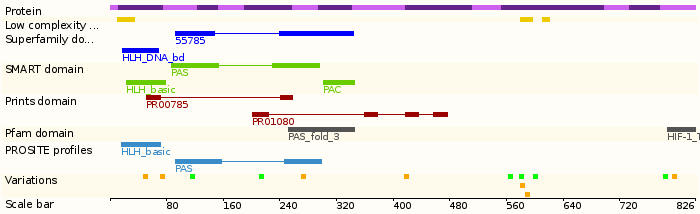
- Pathways: Erythropoietin mediated neuroprotection through NF-kB
- Hypoxia and p53 in the Cardiovascular system
- Hypoxia-Inducible Factor in the Cardiovascular System
- VEGF, Hypoxia, and Angiogenesis
- Interactions:

- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB017442
- OMIM: 603348
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy