Alias (According to NCBI)
- CD222
- CIMPR
- M6P-R
- MPRI
- Insulin-like growth factor-2 receptor (mannose-6-phosphate receptor, cation-independent)
- cation-independent mannose-6 phosphate receptor
- insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor
- Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor precursor (CI Man-6-P receptor) (CI-MPR) (Insulin-like growth factor II receptor) (300 kDa mannose 6-phosphate receptor) (MPR 300) (MPR300) (CD222 antigen)
Description
(According to SwissProt)
CD222 is a 250kDa transmembrane protein with a short cytoplasmic tail containing an internalization signal. CD222 was originally identified as a receptor for IGFII and M6P-containing proteins (e.g. lysosomal hydrolases). Lysosomal enzymes are sorted to lysosomes via CD222 either from the Golgi, where the enzymes acquire M6P, or from the extracellular space. The majority of CD222 molecules (approximately 90-95%) are located intracellularly, only 5-10% is present on the cell membrane. The internalization rate seems to be enhanced by ligand induced dimerization of CD222 as well as by phosphorylation of its cytoplasmic serine. CD222 is also a receptor for TGFbeta latency associated peptide (LAP), proliferin and may bind several molecules independently of M6P, including plasminogen, CD87 or retinoic acid. It is involved in activation of latent TGFbeta.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location:6q26
- Orientation: Plus strand
- Size: 137,452 bases
- 48 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_007422

CGH (6q26): Losses (%) -6.1 Gain (%) 3.4
- HGMD:
- SNPs: IGF2R
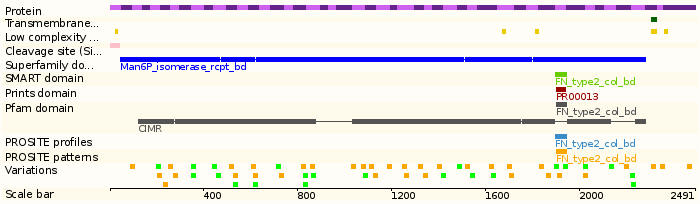
- Size:2491 amino acids; 274306 Da
- Sub cellular location: Type I membrane protein. Lysosomal
- Protein domains:
- Pathways:
- Interactions: P11717
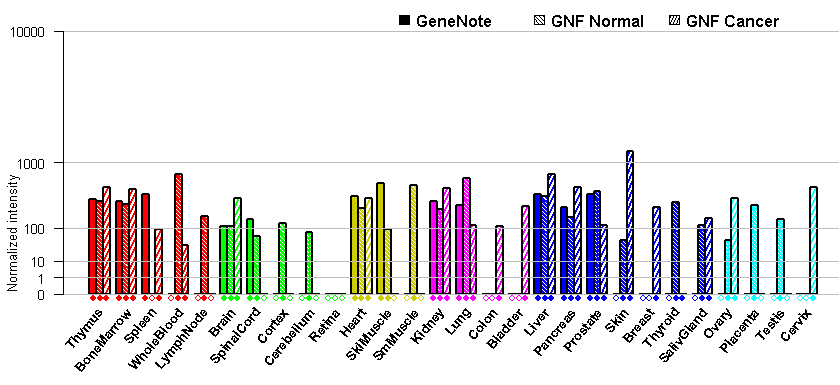
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB009661
- OMIM:147280
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy