|
|
- CK6B
- HGNC:6464
- KRTL1
- PC2
- cytokeratin 6B
- keratin, epidermal, type II, K6B
- keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6B
- keratin-like 1 (a type II keratin
sequence)
- Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6B (Cytokeratin
6B) (CK 6B) (K6b keratin).
|
|
|
- The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin gene family. The type
II cytokeratins consist of basic or neutral proteins which are arranged in pairs of
heterotypic keratin chains coexpressed during differentiation
of simple and stratified epithelial tissues. As many as six of this type II cytokeratin
(KRT6) have been identified; the multiplicity of the genes is attributed to successive
gene duplication events. The genes are expressed with family members KRT16 and/or KRT17 in
the filiform papillae of the tongue, the stratified epithelial
lining of oral mucosa and esophagus, the outer root sheath of hair follicles, and the
glandular epithelia. Mutations in these genes have been associated with pachyonychia congenita. The type II
cytokeratins are clustered in a region of chromosome 12q12-q13.
|
|
|
- Location: 12q12-q13
- Orientation: minus strand
- Size: 5,473 bases
- 9 Exons
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000012.

· CGH (12q12-13): Losses (%) -1.7 Gain
(%) 7.8 |
- Mutations and SNPs (According
to HGMD and SNP)
|
|
|
|
·
mRNA
sequence (Human): NM_005555.
·
Size: 2218 bp
·
cDNA libraries: KRT6B
|
|
|
·
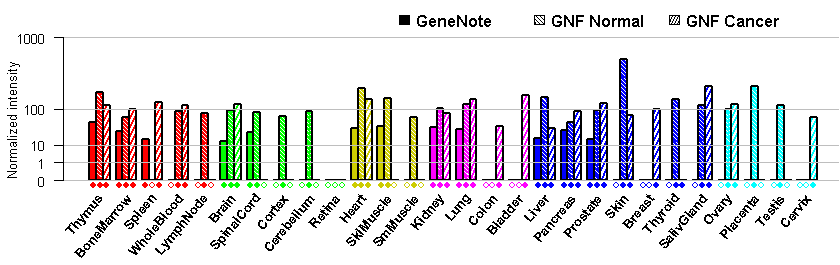
Subcellular location: intracellular,
cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, intermed filament
·
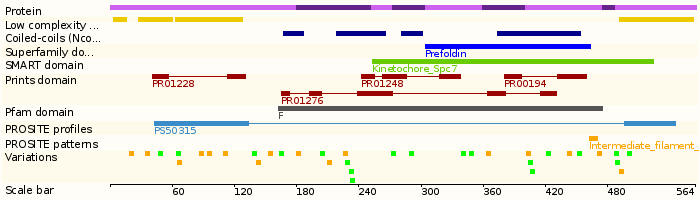
Protein domains
·
Protein sequence (Human): P04259
·
Homologous genes:: KRT6B
·
2D PAGE P04259
·
3D Structure:
|
|
|
·
Pathway:
·
Protein interactions:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

