Alias (According to NCBI)
- 37LRP
- 67LR
- LAMB2
- RPSA
- p40
- 67kD, ribosomal protein SA
- laminin receptor 1 (67kD)
- laminin receptor 1 (67kD, ribosomal protein SA)
- laminin receptor 1 (ribosomal protein SA, 67kDa)
- 40S ribosomal protein SA (p40) (34/67 kDa laminin receptor) (Colon
carcinoma laminin-binding
protein) (NEM/1CHD4) (Multidrug resistance- associated protein MGr1-Ag).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide variety of biological processes including cell adhesion, differentiation, migration, signaling, neurite outgrowth and metastasis. Many of the effects of laminin are mediated through interactions with cell surface receptors. These receptors include members of the integrin family, as well as non-integrin laminin-binding proteins. This gene encodes a high-affinity, non-integrin family, laminin receptor 1. This receptor has been variously called 67 kD laminin receptor, 37 kD laminin receptor precursor (37LRP) and p40 ribosome-associated protein. The amino acid sequence of laminin receptor 1 is highly conserved through evolution, suggesting a key biological function. It has been observed that the level of the laminin receptor transcript is higher in colon carcinoma tissue and lung cancer cell line than their normal counterparts. Also, there is a correlation between the upregulation of this polypeptide in cancer cells and their invasive and metastatic phenotype. Multiple copies of this gene exist, however, most of them are pseudogenes thought to have arisen from retropositional events. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 3p21.3
Orientation: plus strand - Size:5721 bp
- 7 exons
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000003
![]()
CGH (3p21.3): Losses (%) -29.1 Gain (%) 0.6
- HGMD :
- SNPs: LAMR1
mRNA sequence (Human): NM_001012321 ,NM_002295
Size:1109 bp , 1173 bp
cDNA libraries: LAMR1
- Size:294 amino acids; 32723 Da
- Catalytic activity:
- Subcellular location: Cytoplasmic.
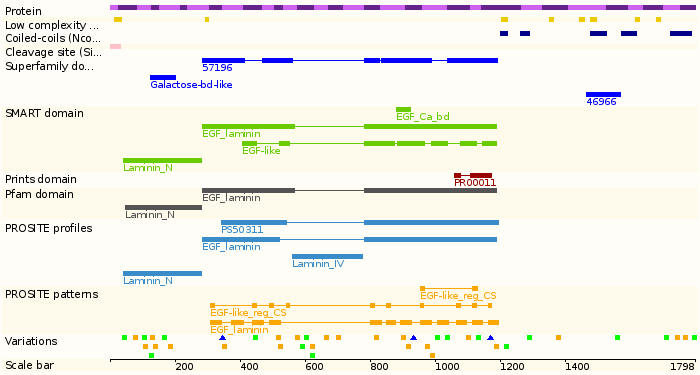
Protein domains
Pathway:
Protein interactions:
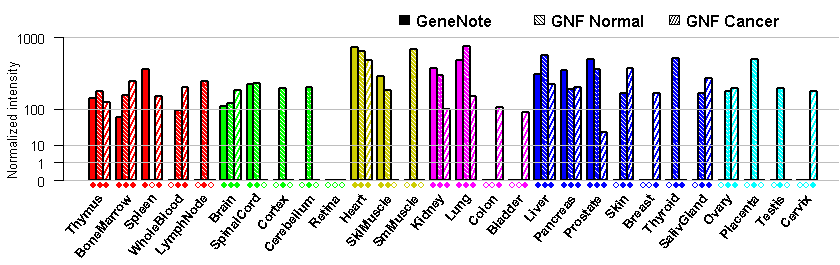
- Tissue expression:
OMIM: 150370
PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy