Alias (According to NCBI)
- ARIA
- GGF
- GGF2
- HGL
- HRG
- HRGA
- NDF
- SMDF
- glial growth factor
- heregulin, alpha (45kD, ERBB2 p185-activator)
- neu differentiation factor
- neuregulin 1
- sensory and motor neuron derived factor
- Neuregulin-1, sensory and motor neuron-derived factor isoform.
- Pro-neuregulin-1 precursor (Pro-NRG1)
[Contains: Neuregulin-1 (Neu differentiation factor)
(Heregulin) (HRG) (Breast cancer cell differentiation factor p45) (Acetylcholine receptor inducing
activity) (ARIA) (Sensory and motor neuron-derived factor) (Glial growth factor)].
Description
(According to SwissProt)
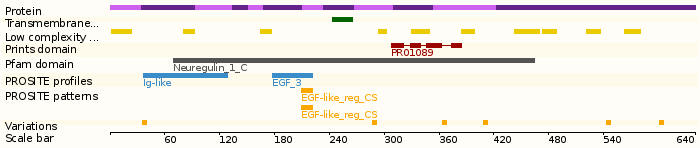
- Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) was originally identified as a 44-kD glycoprotein that interacts with the NEU/ERBB2 receptor tyrosine kinase to increase its phosphorylation on tyrosine residues. It is known that an extraordinary variety of different isoforms are produced from the NRG1 gene by alternative splicing. These isoforms include heregulins (HRGs), glial growth factors (GGFs) and sensory and motor neuron-derived factor (SMDF). They are tissue-specifically expressed and differ significantly in their structure. The HRG isoforms all contain immunoglobulin (Ig) and epidermal growth factor-like (EGF-like) domains. GGF and GGF2 isoforms contain a kringle-like sequence plus Ig and EGF-like domains; and the SMDF isoform shares only the EGF-like domain with other isoforms. The receptors for all NRG1 isoforms are the ERBB family of tyrosine kinase transmembrane receptors. Through interaction with ERBB receptors, NRG1 isoforms induce the growth and differentialtion of epithelial, neuronal, glial, and other types of cells.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location:8p12
- Orientation: plus strand
- Size: 216321 bp
- 3 exons
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000008.
![]()
CGH (8p12): Losses (%) - 12.8 Gain (%) 6.7
- HGMD :
- SNPs: NRG1
- Size: 296 amino acids; 31685 Da
- Catalytic activity:
Subcellular location: Secreted. May possess an internal uncleaved signal sequence.
Protein domains
Pathway:
Neuroregulin receptor degredation protein-1 Controls ErbB3 receptor recycling
Protein interactions:
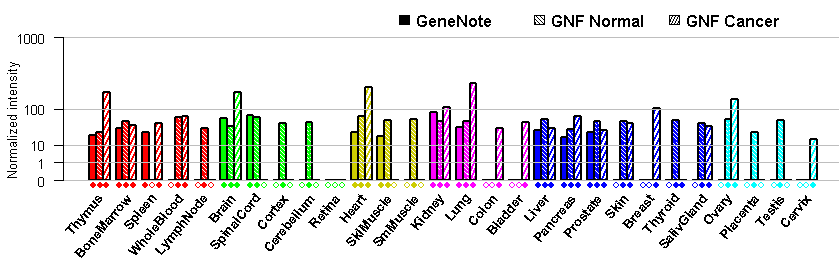
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB002304