Alias (According to NCBI)
- ARF
- CDK4I
- CDKN2
- CMM2
- INK4
- INK4a
- MLM
- MTS1
- P16
- TP16
- p14
- p14ARF
- p16INK4
- p16INK4a
- p19
- CDK4 inhibitor p16-INK4
- cell cycle negative regulator beta
- cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (melanoma, p16, inhibits CDK4)
- cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, p14ARF
- cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p12, p16INK4a alternatively spliced form
- cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16
- multiple tumor suppressor 1
- Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibitor A (CDK4I) (p16-INK4) (p16-INK4a) (Multiple tumor suppressor 1) (MTS1).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
- This gene generates several transcript variants which differ in their first exons. At least three alternatively spliced variants encoding distinct proteins have been reported, two of which encode structurally related isoforms known to function as inhibitors of CDK4 kinase. The remaining transcript includes an alternate first exon located 20 Kb upstream of the remainder of the gene; this transcript contains an alternate open reading frame (ARF) that specifies a protein which is structurally unrelated to the products of the other variants. This ARF product functions as a stabilizer of the tumor suppressor protein p53 as it can interact with, and sequester, MDM1, a protein responsible for the degradation of p53. In spite of the structural and functional differences, the CDK inhibitor isoforms and the ARF product encoded by this gene, through the regulatory roles of CDK4 and p53 in cell cycle G1 progression, share a common functionality in cell cycle G1 control. This gene is frequently mutated or deleted in a wide variety of tumors, and is known to be an important tumor suppressor gene.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 9p21
- Orientation: minus strand
- Size: 26,739 bp
- 4 exons
- DNA sequence (Human): NC_000009
![]()
- CGH (9p21.3): Losses (%) - 30.7 Gain (%) 7.3
- HGMD : CDKN2A
- SNPs: CDKN2A
- Size: 156 amino acids; 16532 Da
- Catalytic activity:
- Subcellular location:
- Protein domains
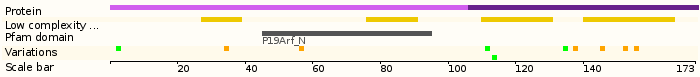
Pathway:
- Cell Cycle: G1/S Check Point
- Cyclins and Cell Cycle Regulation
- Tumor Suppressor Arf Inhibits Ribosomal Biogenesis
Protein interactions: 6108N
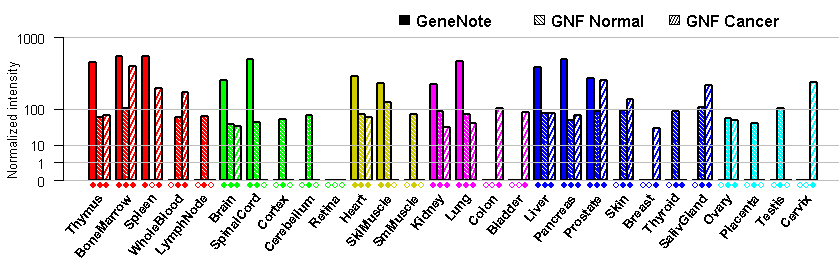
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB000093
OMIM: 600160
PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy