Alias (According to NCBI)
- UPA
- URK
- U-plasminogen activator
- plasminogen activator, urinary
- plasminogen activator, urokinase
- urokinase-type plasminogen activator precursor
- Urokinase-type plasminogen activator precursor (EC 3.4.21.73) (uPA) (U-plasminogen activator).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
This gene encodes a serine protease involved in degradation of the extracellular matrix and possibly tumor cell migration and proliferation. A specific polymorphism in this gene may be associated with late-onset Alzheimer disease and also with decreased affinity for fibrin-binding. The protein encoded by this gene converts plasminogen to plasmin by specific cleavage of an Arg-Val bond in plasminogen. This gene's proprotein is cleaved at a Lys-Ile bond by plasmin to form a two-chain derivative in which a single disulfide bond connects the amino-terminal A-chain to the catalytically active, carboxy-terminal B-chain. This two-chain derivative is also called HMW-uPA (high molecular weight uPA). HMW-uPA can be further processed into LMW-uPA (low molecular weight uPA) by cleavage of chain A into a short chain A (A1) and an amino-terminal fragment. LMW-uPA is proteolytically active but does not bind to the uPA receptor.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
CGH (10q24): Losses (%) - 9.5 Gain (%) 1.7
- HGMD:
- SNPs: PLAU
- Size: 431 amino acids; 48525 Da
- Catalytic activity: Specific cleavage of Arg-|-Val bond in plasminogen to form plasmin.
Subcellular location:
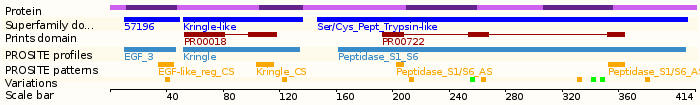
Protein domains
Pathway:
Protein interactions: 137N

OMIM:
PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy