Alias (According to NCBI)
- 1-phosphatidyl-D-myo-inositol-4,5-bisphosphate
- PLC-II
- PLC-gamma-1
- PLC1
- PLC148
- PLCgamma1
- inositoltrisphosphohydrolase
- 1-phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma 1
- monophosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase
- phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C
- phosphoinositidase C
- phosphoinositide phospholipase C
- phospholipase C, gamma 1
- phospholipase C, gamma 1 (formerly subtype 148)
- phospholipase C-148
- triphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase
- 1-phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma 1 (EC 3.1.4.11) (Phosphoinositide phospholipase C) (PLC-gamma-1) (Phospholipase C-gamma-1) (PLC-II) (PLC-148)
Description
(According to SwissProt)
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and diacylglycerol from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. This reaction uses calcium as a cofactor and plays an important role in the intracellular transduction of receptor-mediated tyrosine kinase activators. For example, when activated by SRC, the encoded protein causes the Ras guanine nucleotide exchange factor RasGRP1 to translocate to the Golgi, where it activates Ras. Also, this protein has been shown to be a major substrate for heparin-binding growth factor 1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor)-activated tyrosine kinase.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 20q12-q13.1
- Orientation: Plus strand
- Size: 38,196 bases
- 32 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_011362
![]()
CGH (20q12-13): Losses (%) - 1.7 Gain (%) 19.0
- HGMD:
- SNPs: PLCG1
- Size:1290 amino acids; 148531 Da
- Catalytic activity: 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5- bisphosphate + H(2)O = D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate + diacylglycerol
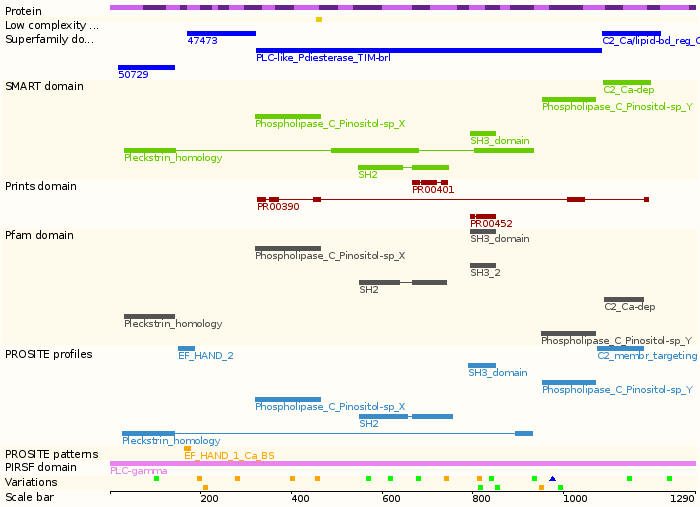
- Protein domains:
- Pathways: Wnt signaling pathway
- Inositol phosphate metabolism
- Phosphatidylinositol signaling system
- Interactions: 100N

- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB004277
- OMIM: 172420
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy