Alias (According to NCBI)
- FAP-1
- PNP1
- PTP-BAS
- PTP-BL
- PTP1E
- PTPL1
- PTPLE
- APO-1/CD95 (Fas)-associated phosphatase
- Fas-associated phosphatase-1
- protein tyrosine phosphatase 1E
- protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 13 (APO-1/CD95 (Fas)-associated phosphatase)
- protein tyrosine phosphatase, nonreceptor type 13
- protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1, Fas-associated
- protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPL1
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 13 (EC 3.1.3.48) (Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1E) (PTP-E1) (hPTPE1) (PTP-BAS) (Protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPL1) (Fas-associated protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1) (FAP-1).
Description
(According to SwissProt)
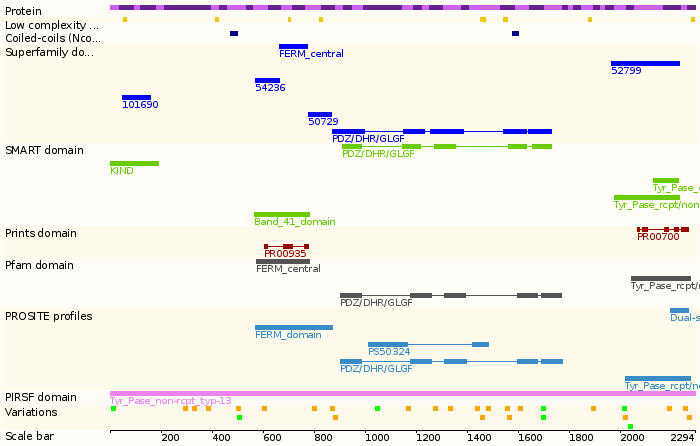
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP is a large protein that possesses a PTP domain at C-terminus, and multiple noncatalytic domains, which include a domain with similarity to band 4.1 superfamily of cytoskeletal-associated proteins, a region consisting of five PDZ domains, and a leucine zipper motif. This PTP was found to interact with, and dephosphorylate Fas receptor, as well as Ikappa Balpha through the PDZ domains, which suggested its role in Fas mediated programmed cell death. This PTP was also shown to interact with GTPase-activating protein, and thus may function as a regulator of Rho signaling pathway.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location:4q21.3
- Orientation: Plus strand
- Size: 220,417 bases
- 17 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_016354

- CGH (4q21.3): Losses (%) - 18.4 Gain (%) 2.2
- HGMD :
- SNPs: PTPN13
- Size: 2485 amino acids,116150.07 Da
- Catalytic activity:
Subcellular location:
- Protein domains:
- Pathways: FAS signaling pathway ( CD95 )
- Interactions:
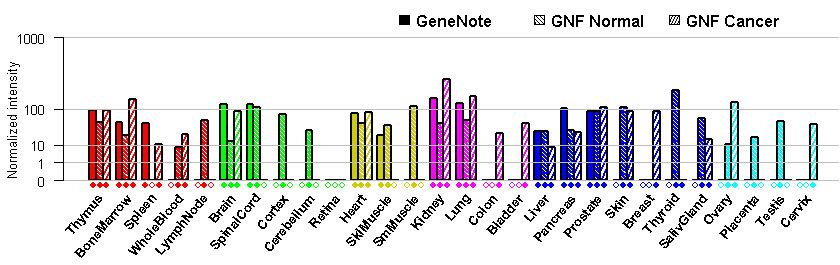
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA): CAB002213
- OMIM:600267
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy