Alias (According to NCBI)
- FBL1
- FBXL1
- FLB1
- MGC1366
- CDK2/cyclin A-associated protein p45
- S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (p45)
- S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (F-box protein Skp2) (Cyclin
A/CDK2-associated protein p45)
(p45skp2)
Description
(According to SwissProt)
This gene encodes a member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the F-box. The F-box proteins constitute one of the four subunits of ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SCFs (SKP1-cullin-F-box), which function in phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination. The F-box proteins are divided into 3 classes: Fbws containing WD-40 domains, Fbls containing leucine-rich repeats, and Fbxs containing either different protein-protein interaction modules or no recognizable motifs. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Fbls class; in addition to an F-box, this protein contains 10 tandem leucine-rich repeats. This protein is an essential element of the cyclin A-CDK2 S-phase kinase. It specifically recognizes phosphorylated cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (CDKN1B, also referred to as p27 or KIP1) predominantly in S phase and interacts with S-phase kinase-associated protein 1 (SKP1 or p19). In addition, this gene is established as a protooncogene causally involved in the pathogenesis of lymphomas.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location:5p13
- Orientation: Plus strand
- Size: 31,958 bases
- 10 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_006576
![]()
CGH (5p13): Losses (%) -5.6 Gain (%) 12.8
- HGMD:
- SNP: SKP2
- Size: 424 amino acids, 47760 Da
- Catalytic activity:
- Subcellular location:
- Protein domains:
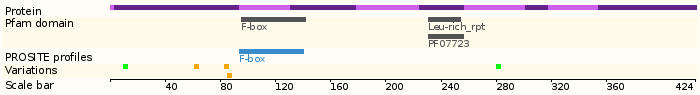

- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA) : CAB013533
- OMIM: 601436
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy