Alias (According to NCBI)
- EST2 (LL)
- TCS1 (LL)
- TP2 (LL)
- TRT (LL)
- hEST2 (LL)
- hTERT (GDB)
- telomerase catalytic subunit (LL)
- telomerase reverse transcriptase (GDB, LL, HUGO)
- Telomerase reverse transcriptase (EC 2.7.7.-) (Telomerase catalytic subunit) (HEST2)
Description
(According to SwissProt)
Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein polymerase that maintains telomere ends by addition of the telomere repeat TTAGGG. The enzyme consists of a protein component with reverse transcriptase activity, encoded by this gene, and an RNA component which serves as a template for the telomere repeat. Telomerase expression plays a role in cellular senescence, as it is normally repressed in postnatal somatic cells resulting in progressive shortening of telomeres. Deregulation of telomerase expression in somatic cells may be involved in oncogenesis. Studies in mouse suggest that telomerase also participates in chromosomal repair, since de novo synthesis of telomere repeats may occur at double-stranded breaks. Alternatively spliced variants encoding different isoforms of telomerase reverse transcriptase have been identified; the full-length sequence of some variants has not been determined. Alternative splicing at this locus is thought to be one mechanism of regulation of telomerase activity.
- Chromosomal location
(According to NCBI, CGH: progenetix)
- Location: 5p15.33
- Orientation: Minus strand
- Size: 41,877 bases
- 16 Exons
- DNA Sequence: NT_023089
![]()
CGH (5p15.33): Losses (%) -2.2 Gain (%) 16.2
- Size: 1132 amino acids; 126996 Da
- Catalytic activity:
- Sub cellular location: Nuclear
- Protein domains:

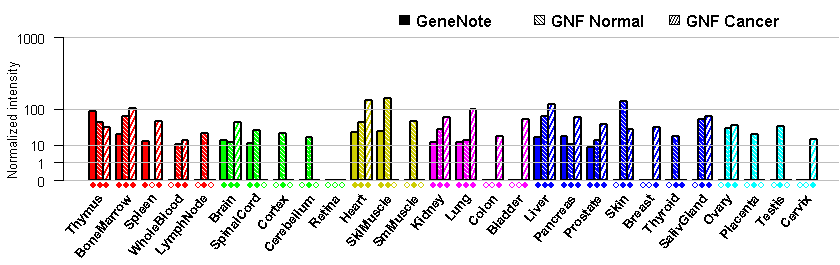
- Tissue expression: PubMed Reference
- Human Protein Atlas (HPA) : TERT
- OMIM:187270
- PubMed: Early detection Diagnosis Prognosis Therapy